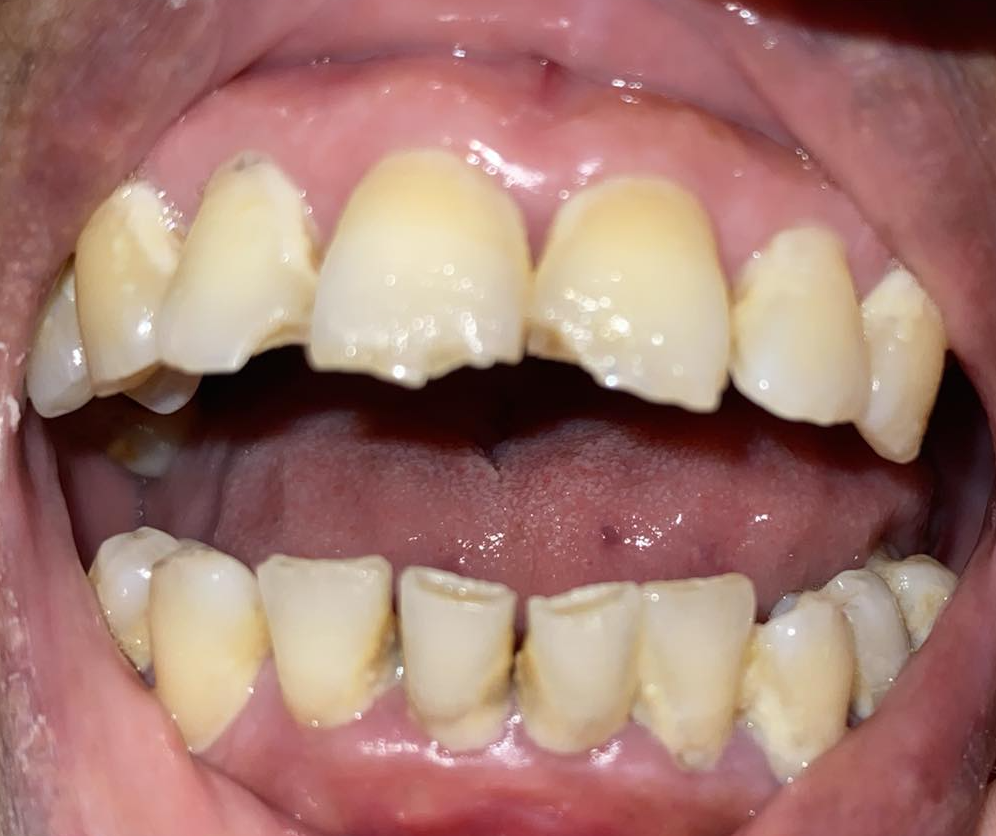
How to Stop Bleeding Gums after Quitting Smoking
You can stop bleeding gums after quitting smoking by getting a deep cleaning from your dentist, improving your oral hygiene, swishing antibacterial mouthwash and using other adjuncts to augment self-performed mechanical plaque removal, living a healthier lifestyle, and taking vitamins to promote the healing of your inflamed gums.
Blood is a universal cause of panic, especially when it comes right out of our mouths. Even if we don’t feel any pain and only see blood when we brush our teeth, many consider this phenomenon alarming. If you have observed recently that your gums are bleeding excessively after quitting smoking, and you need to know more about this condition, this article would be your best guide.
How long after stopping smoking do gums stop bleeding?
Bleeding gums is a sign of gum disease, specifically gingivitis or periodontitis, which is often exacerbated by smoking. When you quit smoking, your body’s healing process begins to improve, including your oral health. Generally, the time it takes for gums to stop bleeding after quitting smoking can vary based on individual health factors and the severity of any pre-existing gum disease.
Given that you have quit smoking, you’ve been brushing thrice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush, and you’re visiting your dentist at least twice a year, here are the changes that you can expect in your gums:
- Immediate Changes: Within a few days of quitting, the blood flow to your gums and oral tissues improves.
- Short-term Changes (1-2 weeks): Inflammation may begin to decrease, and the immune response can start to normalize, leading to less bleeding.
- Long-term Changes (1-3 months): Gums can continue to heal, and bleeding should significantly reduce or stop altogether if proper oral hygiene is maintained.
Regular dental cleanings, good oral hygiene practices, and possibly professional treatments may be necessary for optimal recovery. If gum bleeding persists, it’s important to consult a dentist, as this may indicate underlying issues that need professional attention.
When do gums go back to normal after quitting smoking?
According to previous studies, gums go back to normal 11 years after quitting smoking. Moreover, research done by Tomar and Asma in 2000 has proven that the likelihood or probability of having periodontitis for those who have quit smoking for over 11 years is almost the same as for non-smokers.
It’s essential to maintain regular dental check-ups and cleanings, practice good oral hygiene (brushing twice a day, flossing daily), and follow any additional recommendations from your dentist or dental hygienist.
If you notice any persistent issues with your gums, such as continued bleeding or inflammation, it’s important to consult with a dental professional for further evaluation and treatment.
How do I stop my gums from bleeding asap?
You can stop your gums from bleeding once you recognize the disease you have and what’s causing it. Bleeding gums may mean that you have gingivitis, the condition where your gums are inflamed and infected by your oral microbiota (sounds boring, but it’s all the bacteria in your mouth) specifically the ones that are in your plaque.
A recent meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) in 2019 conducted by Worthington HV, et. al. in 2019 concluded that these are the things that can help stop your gums from bleeding ASAP:
Self-Performed Mechanical Removal of Plaque
The term “self-performed mechanical removal of plaque” might sound complex, but it’s actually quite simple. It involves:
- Brushing Your Teeth Properly: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush at least twice a day, making sure to clean all surfaces of your teeth.
- Regular Use of Dental Floss and Interdental Brushes: Since your toothbrush can only reach up to 0.9mm subgingivally, given that you have angulated it properly, flossing or brushing with interdental brushes in between your teeth could help in getting rid of interproximal plaque. Do this once daily to ensure the cleanliness of your mouth.
- Tongue Scraping: Use a tongue scraper or your toothbrush to clean your tongue and reduce bacteria buildup.
Bleeding gums are a sign of inflammation, often caused by plaque buildup. Plaque is a soft, milky-yellowish substance that sticks to the surfaces of your oral cavity, including your teeth, gums, palate, and tongue. To prevent gum inflammation, it’s crucial to diligently remove plaque through proper oral hygiene practices.
Adjunctive Chemical Removal of Plaque
We have established that plaque is the cause of gingivitis or the inflammation of your gums, and we can effectively remove it when we remove it manually by toothbrushing or flossing daily. However, for cases with severe gum bleed, another way to stop this from happening is the use of mouthwash.
Mouthwash can be beneficial in addressing gum bleeding through several mechanisms:
Reduces Bacteria:
Antibacterial mouthwashes, such as those containing chlorhexidine or essential oils, help reduce the bacterial load in your mouth. This decrease in bacteria helps lower the risk of gum inflammation and bleeding.
Reduces Plaque: Mouthwashes can help remove and prevent the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth and gums. Less plaque means less irritation and inflammation, which can reduce gum bleeding.
Reduces Inflammation: Anti-inflammatory ingredients in some mouthwashes can help soothe inflamed gums, leading to reduced bleeding.
Promotes Healing: Mouthwashes with ingredients like hydrogen peroxide can promote healing of oral tissues, including gums, which can help stop bleeding over time.
Improves Oral Hygiene: Using mouthwash as part of your daily oral hygiene routine helps reach areas that brushing and flossing might miss, providing a more thorough cleaning and reducing the factors that contribute to gum bleeding.
How to Use Mouthwash for Best Results:
Choose the Right Mouthwash: Look for an antibacterial or antiseptic mouthwash. Consult with your dentist for recommendations based on your specific needs.
Use It Correctly: Follow the instructions on the mouthwash label. Generally, rinse for about 30 seconds and avoid eating or drinking for at least 30 minutes afterward to allow the active ingredients to work effectively.
Maintain a Regular Routine: Use mouthwash as part of your daily oral care routine, in addition to brushing and flossing.
How do you heal your gums after smoking?
Just like your skin, it takes a while before your gums heal after you quit smoking. As stated earlier, it would take over 11 years for a smoker to achieve the healthy condition of the gums similar to those that are non-smokers. However, you can hasten the process of healing your gums after smoking if you quit smoking as soon as possible.
Here are some steps you can take to promote the healing in your gums:
1. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene:
Brush Properly: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush. Make sure to brush along the gum line to remove plaque.
Floss Daily: Flossing helps remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and under the gum line.
Use Mouthwash: An antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria and inflammation in your gums.
2. Professional Dental Care:
Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings. Your dentist can remove plaque and tartar buildup and monitor your gum health.
Deep Cleaning: If necessary, your dentist may recommend scaling and root planing, a deep cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line.
3. Healthy Diet:
Nutrient-Rich Foods: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods provide essential vitamins and minerals that support gum health.
Avoid Sugary and Acidic Foods: Reduce consumption of sugary and acidic foods and drinks, which can contribute to plaque buildup and gum disease.
4. Stay Hydrated:
Drink Plenty of Water: Water helps wash away food particles and bacteria, and it keeps your mouth hydrated.
5. Quit Smoking Permanently:
Avoid All Forms of Tobacco: Continued use of tobacco products, even in reduced amounts, can hinder the healing process and increase the risk of gum disease and other oral health issues.
6. Use a Salt Water Rinse:
Rinse with Salt Water: Mix a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth with it. This can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
7. Manage Stress:
Stress Reduction: High stress levels can affect your immune system and overall health. Practice stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, or yoga.
8. Consider Supplements:
Vitamin C and Coenzyme Q10: These supplements can support gum health and healing. Consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
9. Stay Committed:
Consistency is Key: Healing takes time, so be patient and consistent with your oral care routine.
By following these steps and working closely with your dental professional, you can help your gums heal and improve your overall oral health after quitting smoking.
Why are my gums worse after quitting smoking?
Smokers are 50% more likely to develop periodontal disease than non-smokers, however, smoking also causes your capillaries or the small blood vessels in your gums to constrict, which makes it less likely to bleed.
Once you quit your smoking habits, the blood vessels in your gums will eventually heal and revert to their original size to promote further healing and allow more blood flow in your gums.
Experiencing worsened gum issues after quitting smoking can be concerning, but it’s not uncommon. Here are some reasons why your gums might seem worse after quitting smoking:
1. Improved Blood Circulation:
- Increased Blood Flow: Smoking constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the gums. When you quit, blood flow improves, leading to increased inflammation and bleeding as the gums start to heal and respond to existing issues.
2. Heightened Immune Response:
- Better Immune Function: Smoking suppresses the immune system. After quitting, your immune system becomes more active, which can initially increase inflammation as your body starts fighting off existing infections more effectively.
3. Revealed Damage:
- Hidden Problems Become Visible: Smoking can mask the symptoms of gum disease by reducing blood flow and inflammation. After quitting, these underlying issues can become more apparent as the gums start to heal.
4. Plaque and Tartar Buildup:
- Existing Build-up: If there was a significant buildup of plaque and tartar while you were smoking, this can contribute to ongoing gum issues. Improved blood flow and immune response can make this buildup more problematic.
5. Withdrawal Symptoms:
- Changes in Oral Environment: Quitting smoking can lead to dry mouth and changes in saliva production, which can temporarily affect your oral health and make your gums more susceptible to issues.
Steps to Address Worsening Gum Issues:
- Maintain Excellent Oral Hygiene:
- Brush and Floss Regularly: Brush twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and prevent further gum issues.
- Use Antibacterial Mouthwash: This can help reduce bacteria and inflammation.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Drink Water: Keeping your mouth hydrated can help with dry mouth and overall oral health.
- Visit Your Dentist:
- Professional Cleaning: Schedule a dental check-up and cleaning to remove any plaque and tartar buildup and assess your gum health.
- Follow Professional Advice: Your dentist can provide personalized recommendations and treatments if necessary.
- Use a Salt Water Rinse:
- Rinse with Salt Water: This can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Eat a Healthy Diet:
- Nutrient-Rich Foods: Consume a diet rich in vitamins and minerals that support gum health, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Be Patient:
- Healing Takes Time: Understand that your gums are going through a healing process. It might take some time for them to fully recover and for symptoms to improve.
Will my teeth recover if I stop smoking?
Quitting smoking can have a positive impact on your oral health, including your teeth. While some damage from smoking may be irreversible, many aspects of your oral health can improve significantly. Here’s how your teeth can recover after you stop smoking:
1. Improved Gum Health:
Reduced Inflammation: Quitting smoking reduces inflammation and helps your gums heal, potentially reversing early-stage gum disease (gingivitis).
Better Blood Flow: Improved blood circulation promotes healthier gum tissue and reduces bleeding.
2. Decreased Risk of Tooth Loss:
Stronger Gums and Bones: As your gums and the bone structure supporting your teeth become healthier, the risk of tooth loss decreases.
3. Whiter Teeth:
Stain Reduction: Without the constant exposure to nicotine and tar, your teeth can gradually become whiter. Professional cleanings and whitening treatments can further improve their appearance.
4. Fresher Breath:
Reduced Bad Breath: Quitting smoking helps eliminate the persistent bad breath associated with tobacco use.
5. Lowered Risk of Oral Cancer:
Reduced Carcinogen Exposure: By quitting smoking, you significantly lower your risk of developing oral cancer.
6. Enhanced Healing:
Better Response to Treatment: If you require dental treatments, your body’s improved ability to heal will enhance the effectiveness of these treatments.
Steps to Help Your Teeth Recover After Quitting Smoking:
- Brush Twice Daily: Use fluoride toothpaste and brush at least twice a day.
- Floss Daily: Floss to remove plaque and food particles between your teeth.
- Use Mouthwash: An antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria and freshen your breath.
- Visit Your Dentist Regularly: Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings to monitor and maintain your oral health.
- Professional Treatments: Your dentist can provide treatments like scaling and root planing, whitening, or other procedures to improve your oral health and appearance.
- Nutritious Foods: Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals that support oral health, such as calcium, vitamin C, and vitamin D.
- Limit Sugary Foods: Reduce your intake of sugary and acidic foods and drinks that can contribute to tooth decay.
- Drink Plenty of Water: Water helps wash away food particles and bacteria, and it keeps your mouth hydrated.
- Avoid Staining Foods and Drinks: Limit consumption of coffee, tea, red wine, and other foods and drinks that can stain your teeth.
- Consider Whitening Treatments: Ask your dentist about professional whitening treatments to help remove stains and brighten your smile.
- At-Home Whitening: Over-the-counter whitening products can also be effective, but consult your dentist before use.
By quitting smoking and adopting these healthy habits, you can significantly improve the health and appearance of your teeth and gums. While some damage may be permanent, many aspects of your oral health can recover and greatly benefit from your decision to quit smoking.
Can Ice stop bleeding gums?
Ice can help reduce bleeding gums indirectly by addressing inflammation and swelling, which can contribute to gum bleeding. Ice can reduce inflammation and swelling, which could consequently minimize bleeding.
The coldness of ice could constrain and constrict blood vessels so it reduces blood flow in the area. However, bear in mind that ice is a band-aid solution. You can put ice on the area where you can spot the gum bleeding, but your gums will eventually bleed again under the slightest pressure.
Should I brush my gums if they bleed?
Yes, you should still include your gums in brushing even if they bleed, but you have to ensure that you are using a soft-bristled brush and you are not putting too much pressure on it as you brush.
Image from Quora
For more detailed instructions on how to properly brush your teeth, click here.
Does drinking water help bleeding gums?
Drinking water can indeed help with bleeding gums, though it is not a cure by itself. Here’s how staying hydrated and drinking water can benefit your gums:
1. Hydration:
Maintains Moisture Levels: Keeping your mouth well-hydrated helps to maintain the moisture levels in your gums, reducing the risk of irritation and inflammation that can lead to bleeding.
2. Washes Away Food Particles and Bacteria:
Reduces Plaque: Drinking water helps to wash away food particles and bacteria from your mouth, reducing the buildup of plaque, which is a major cause of gum disease and bleeding.
3. Saliva Production:
Promotes Saliva Flow: Adequate water intake helps to promote saliva production, which is essential for neutralizing acids produced by bacteria in your mouth and for washing away food particles.
4. Dilution of Toxins:
Reduces Toxins: Drinking water can help dilute toxins released by bacteria in the mouth, which can cause irritation and bleeding in the gums.
In conclusion
You can stop bleeding gums after quitting smoking if you improve your oral hygiene habits like brushing your teeth regularly, flossing and swishing mouthwash, visiting your dentist for scheduled dental cleanings, living a healthy lifestyle, and completely quitting your smoking habit.
Remember, the sacrifice that you do today by quitting smoking can still save you for endless health problems in the future, aside from the possible risk of making your prosthodontist rich because you would eventually need complete dentures!



Thank you for some other informative web site. The place else may just I get that kind of information written in such a perfect manner? I’ve a mission that I am just now operating on, and I have been at the glance out for such info.